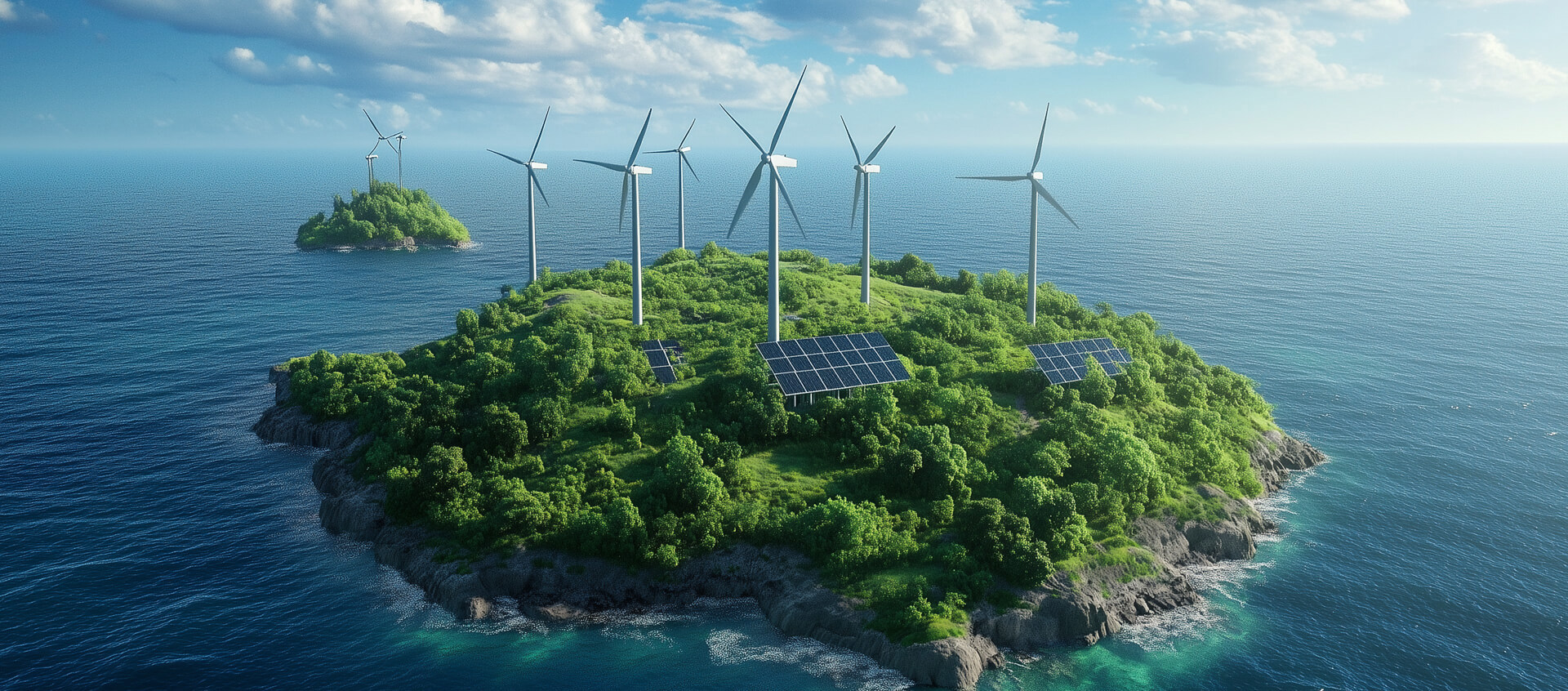

Distributed Negative-Carbon Green Power Plant
3 major application scenarios



Challenges
- Wind and solar power lack stable output due to weather conditions
- Conventional energy storage technology cannot achieve 24-hour continuous power supply
Core Advantages
Providing grid services like rotational inertia, large-scale peak regulation, emergency power including active and reactive

No need for additional transmission facilities

Pure Green Electricity

24/7 power generation

off-grid operation of power plants

Distributed on-site construction

In collaboration with renewable energy sources like wind and solar power
| Power | 100MVV | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration (h) | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 |
| Capacity | 400 | 600 | 800 | 1000 | 1200 |
| Unit Cost(USD/Wh) | 0.32 | 0.72 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.21 |
| At constant power: the longer the duration, the lower the unit cost | |||||
| Capacity | 1000MWh | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration (h) | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 |
| Capacity | 250 | 170 | 125 | 100 | 85 |
| Unit Cost(USD/Wh) | 0.32 | 0.72 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.21 |
| For a given energy capacity, as storage duration increases, the required power ratingdecreases, resulting in reduced unit cost. | |||||

